Dental applications
Dental instruments are possible agents for pathogen transmission.
(CDC guidelines)
If it’s not clean, it shouldn’t be sterilized
Investigators have reported contamination rates of 60% on patient-ready hospital instruments.
Inorganic and organic materials interfere with antimicrobial activity of disinfectants and sterilization.¹
It is impossible to disinfect or even sterilize an inadequately cleaned instrument.² : “Any disinfection process is doomed to fail if cleaning is inadequate”.³
6. Buss et al., 2008, Kovalera et al., 2009
Why worry about dental equipment ?
The importance of cleaning in the decontamination process
If organic soil and biofilm matrix is not removed by the cleaning phase, it is subsequently baked onto the surface of the instrument by the sterilization process, in a vicious circle of contamination that is increasingly difficult to remove.
Centers for Disease Control (CDC) and other regulatory bodies clearly state that instruments should be thoroughly cleaned prior to sterilization for complete risk management.


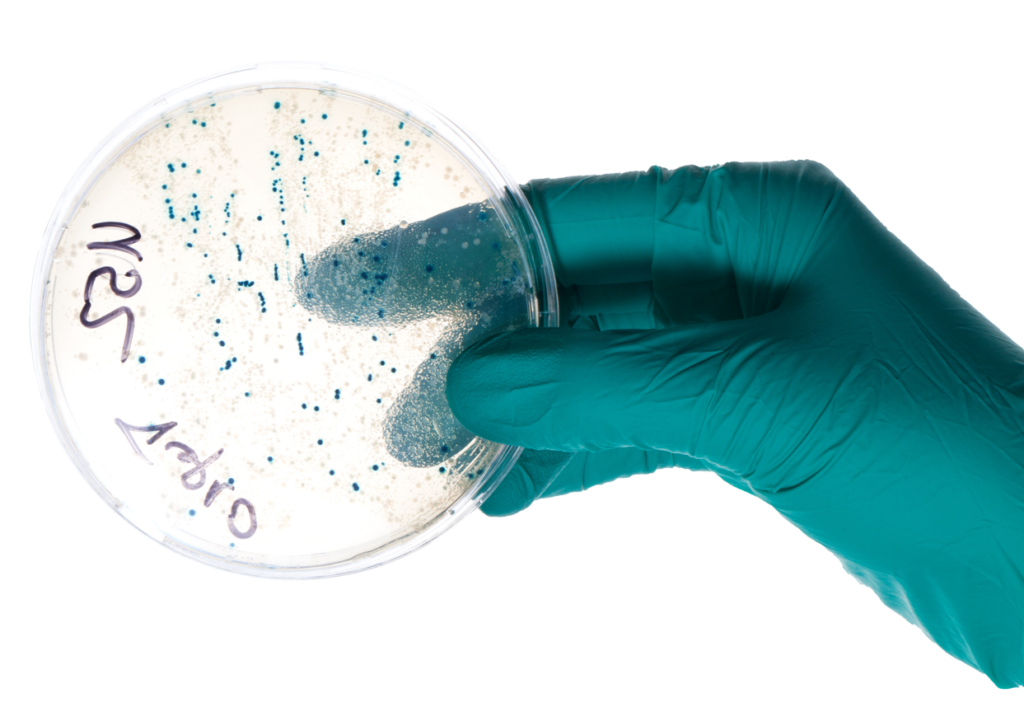
Investigation in dental offices
Tests revealing presence or absence of residual organic contamination were performed on clean, sterilized instruments. Assessment of two dental offices are reported herein :
Protocol: Detection and Removal of Biofilm matrix and Protein contamination
Detection – A patented coloration technique was utilized to reveal presence or absence of organic contamination on selected patient-ready instruments (21 in Dental Office A and 17 in Dental Office B). Instruments were first immersed in a blue colorant for 5 minutes, secondly immersed in an indicator solution for 2 minutes and finally rinsed in clear water. Any remaining blue stains on the surface of the instruments indicate the presence of organic contamination, despite the instruments having been subjected to the decontamination process.
Removal – Following the detection phase, instruments displaying residual contamination were subjected to a 15-minute treatment with OneLife’s high-level detergent in an ultrasound bath at 45°C.
Results
In both dental offices, the detection protocol revealed that 76% of patient-ready instruments were contaminated. This high contamination rate reveals the inadequacy of the cleaning currently in place. The CDC states that such residual organic materials that remain on the surface of instruments interfere with the effectiveness of disinfection and sterilization and should be eliminated. A single treatment with OneLife’s high-level enzymatic detergent reduced the number of contaminated instruments from 76% to 5.8% and 4.8% respectively.
Changing a key parameter of the Sinner Circle and improving the detergent quality removed almost all the contamination. A single treatment with high-level detergent enabled recovery of almost all instruments to their clean state thanks to OneLife’s specific, patented enzymatic compound that completely breaks down organic soil and biofilm matrix.
Other applications

endoscopy
10 to 30% of patient-ready endoscopes are contaminated with microorganisms.

surgical instruments
Over 60% of correctly-processed surgical instruments exhibit residual protein soiling.

surfaces
Working in a safer & cleaner environment is a must. Take control.